-40%
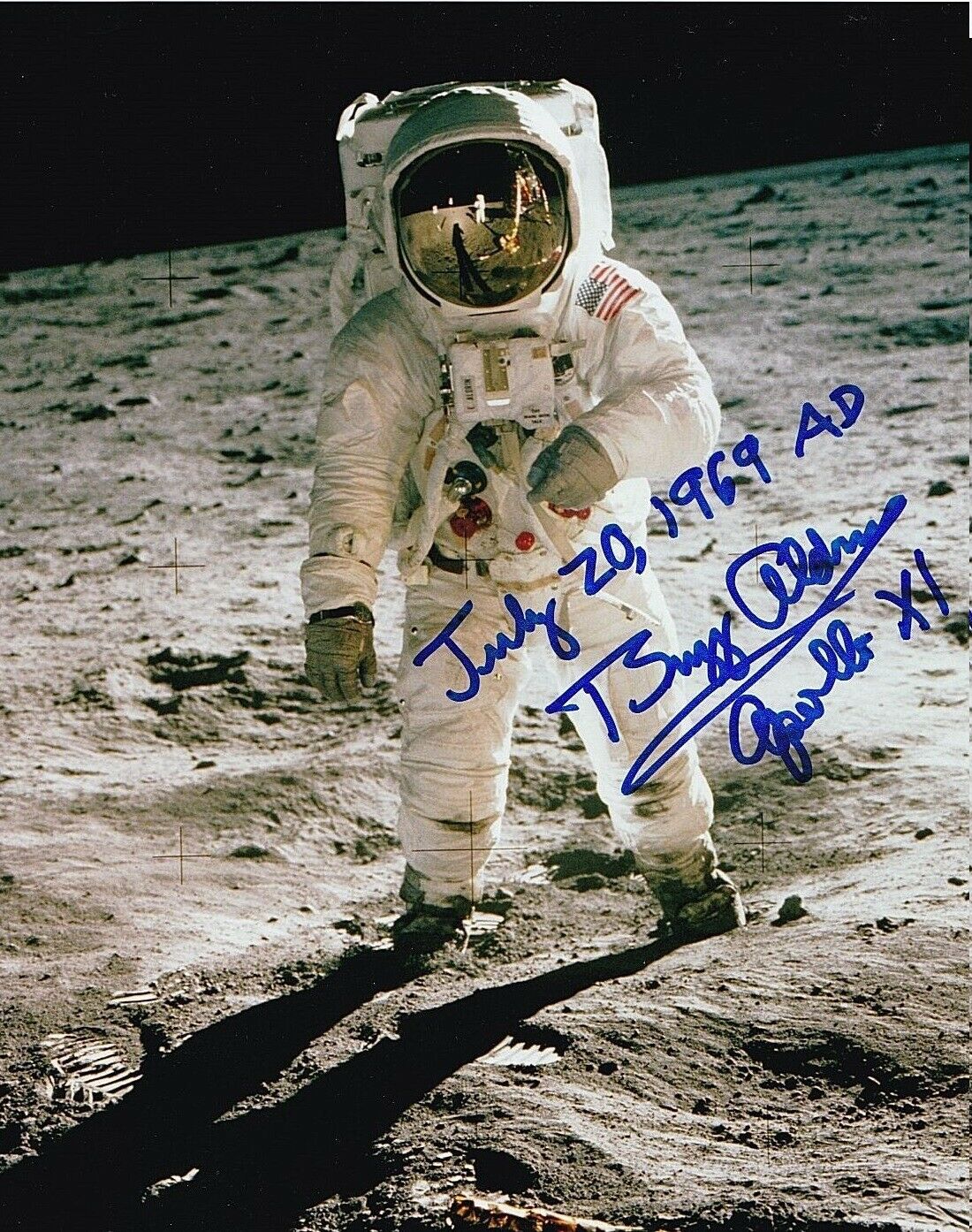
APOLLO LLRV Pilot DON MALLICK AUTOGRAPH,HAND SIGNED
$ 2.64
- Description
- Size Guide
Description
APOLLO LLRV Pilot DON MALLICK AUTOGRAPH,HAND SIGNED8 X 10 LLRV Photo, Signed by APOLLO LLRV Pilot DON MALLICK . ----- This 1964 NASA Flight Reserch Center photograph shows a ground engine test underway on the Lunar Landing Research Vehicle (LLRV) number 1. When Apollo planning was underway in 1960, NASA was looking for a simulator to profile the descent to the Moon's surface. Three concepts surfaced: an electronic simulator, a tethered device, and the ambitious Dryden contribution, a free-flying vehicle. All three became serious projects, but eventually the NASA Flight Research Center's (FRC) Landing Research Vehicle (LLRV) became the most significant one. Hubert M. Drake is credited with originating the idea, while Donald Bellman and Gene Matranga were senior engineers on the project, with Bellman, the project manager. Simultaneously, and independently, Bell Aerosystems Company, Buffalo, N.Y., a company with experience in vertical takeoff and landing (VTOL) aircraft, had conceived a similar free-flying simulator and proposed their concept to NASA headquarters. NASA Headquarters put FRC and Bell together to collaborate. The challenge was; to allow a pilot to make a vertical landing on Earth in a simulated Moon environment, one sixth of the Earth's gravity and with totally transparent aerodynamic forces in a "free flight" vehicle with no tether forces acting on it. Built of tubular aluminum like a giant four-legged bedstead, the vehicle was to simulate a lunar landing profile from around 1500 feet to the Moon's surface. To do this, the LLRV had a General Electric CF-700-2V turbofan engine mounted vertically in gimbals, with 4200 pounds of thrust. The engine, using JP-4 fuel, got the vehicle up to the test altitude and was then throttled back to support five-sixths of the vehicle's weight, simulating the reduced gravity of the Moon. Two hydrogen-peroxide lift rockets with thrust that could be varied from 100 to 500 pounds handled the LLRV's rate of descent and horizontal translations. Sixteen smaller hydrogen-peroxide rockets, mounted in pairs, gave the pilot control in pitch, yaw, and roll. On the LLRV, in case of jet engine failure, six-500-pounds-of thrust rockets could be used by the pilot to carefully apply lift thrust during the rapid descent to hopefully achieve a controllable landing. The pilot's platform extended forward between two legs while an electronics platform, similarly located, extended rearward. The pilot had a zero-zero ejection seat that would then lift him away to safety. Weight and balance design constraints were among the most challenging to meet for all phases of the program (design, development, operations).HE attended Penn State University for college, and served in the United States Navy Reserves, and in 1957 he graduated from the University of Florida with his masters degree in engineering. In 1970 he officially retired from the Navy after achieving the rank of Lieutenant Commander. Mallick served the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics as a test pilot from 1957 - 1963. In 1963 he became a pilot at the Dryden Flight Research Center, and in 1967 he was promoted to Chief Pilot. While there he was a project pilot on both the YF-12 and XB-70A research programs.[2] When Apollo planning was underway in 1960, NASA was looking for a simulator to profile the descent to the Moon's surface. Three concepts surfaced: an electronic simulator, a tethered device, and the ambitious Dryden contribution, a free-flying vehicle. All three became serious projects, but eventually the NASA Flight Research Center’s (FRC) Lunar Landing Research Vehicle (LLRV) became the most significant one. After conceptual planning and meetings with engineers from Bell Aerosystems Company, Buffalo, N.Y., NASA FRC issued a .6 million production contract awarded in 1963, for delivery of the first of two vehicles for flight studies. Built of tubular aluminum alloy like a giant four-legged bedstead, the vehicle was to simulate a lunar landing profile from around 1500 feet to the Moon’s surface. The LLRV had a turbofan engine mounted vertically in a gimbal, with 4200 pounds of thrust. The engine, lifted the vehicle up to the test altitude and was then throttled back to support five-sixths of the vehicle's weight, thus simulating the reduced gravity of the Moon. Two lift rockets with thrust that could be varied from 100 to 500 pounds handled the LLRV's rate of descent and horizontal translations. Sixteen smaller rockets, mounted in pairs, gave the pilot control in pitch, yaw, and roll. The pilot’s platform extended forward between two legs while an electronics platform, similarly located, extended rearward. The pilot had a zero-zero ejection seat that would then lift him away to safety. The two LLRVs were shipped from Bell to the FRC in April 1964, with program emphasis on vehicle No. 1. The first flight, Oct. 30, 1964, NASA research pilot Joe Walker flew it three times for a total of just under 60 seconds, to a peak altitude of approximately 10 feet. By mid-1966 the NASA Flight Research Center had accumulated enough data from the LLRV flight program to give Bell a contract to deliver three Lunar Landing Training Vehicles (LLTVs) at a cost of .5 million each. 1966 ended with the phasing out of the Flight Research Center’s portion of the LLRV program. The LLRV #1 had flown 198 flights, with flight times reaching 9-1/2 minutes and altitudes of around 750 feet. In December 1966 vehicle No. 1 was shipped to NASA Manned Spacecraft Center, followed by No. 2 in mid January 1967 with a total of six flights. The two LLRV’s were soon joined by the three LLTV’s. All five vehicles were relied on for simulation and training of Moon landings. +++++++++++++++++++++++Combining Lots between two auctions, I will be happy to combine two auctions To save you additional postage- Please pay for these lot/lots & postage. If you are successful in the second auction I will bill you for the additional lot, With no additional postage charges. If you do not win any lots in the second auction, I can just ship the lot to you And not have to bill you again, and wait for payment Thank You Sean Marsar
Powered by SixBit's eCommerce Solution